Showcasing Satellite Innovation with a New IP Broadcast Standard


Converged Multimedia Networks
As innovation in the broadcast industry continues, SES recently showcased a groundbreaking on-air demo leveraging the new DVB-NIP (Native IP) and DVB-I standards that are set to change content delivery via satellite.
SES has long been at the forefront of ensuring satellite technology is made simpler for delivering content and has been working with other satellite operators, broadcasters and consumer electronics manufacturers to develop and implement the DVB-NIP specification and most of the satellite related features in DVB-I.
What is DVB-NIP?
![]()
DVB-Native IP (DVB-NIP) is a new international specification developed by the Digital Video Broadcasting Project (DVB), the organization that defines the standards our industry uses for all its satellite-based video and data transmissions.
It is a next generation broadcast system that is inherently and natively IP-based and leverages the same internet technologies available today in all consumer IP media devices. It is also referred to as OTT via satellite.
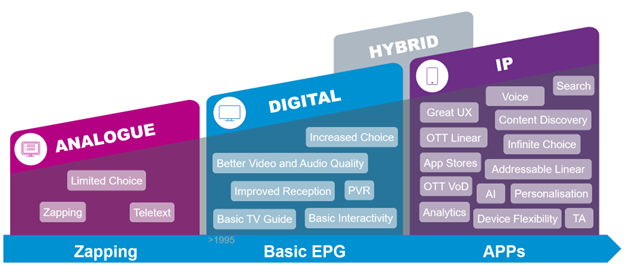
DVB-NIP expands the capabilities of traditional satellite broadcast delivery by bringing content in different formats to all IP devices and providing the multi-device, multi-screen experiences users and customers expect today. DVB-NIP-based broadcasting natively blends with terrestrial unicast broadband content delivery, meaning end users will no longer see whether the data is delivered via broadband or satellite regardless of the platform they chose to watch content on.
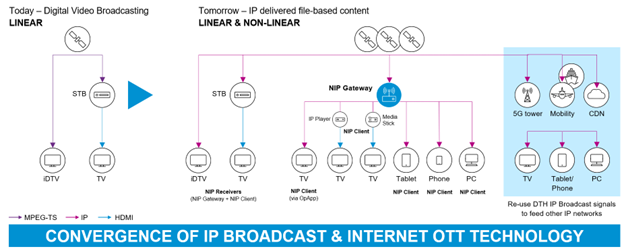
Alongside DVB-NIP, DVB-I is a new DVB protocol specification for television.
![]()
It is a metadata format that describes any type of TV and on-demand video service offering and finds its applications in broadcast, fixed broadband and mobile 5G networks. DVB-I provides, for the first time ever, instant setup features for satellite receivers and a standardised Logical Channel Numbering system for satellite.
DVB-I and DVB-NIP work together to allow for a full convergence of broadcast and OTT technologies into one efficient and contemporary IP media distribution solution.
Showcasing Satellite-Enabled OTT Broadcasting at DVB World 2024
During DVB World 2024, SES showcased its own DVB-NIP Revision 2-compliant in-house software implementation, highlighting the work we’ve done on both DVB-NIP and DVB-I.
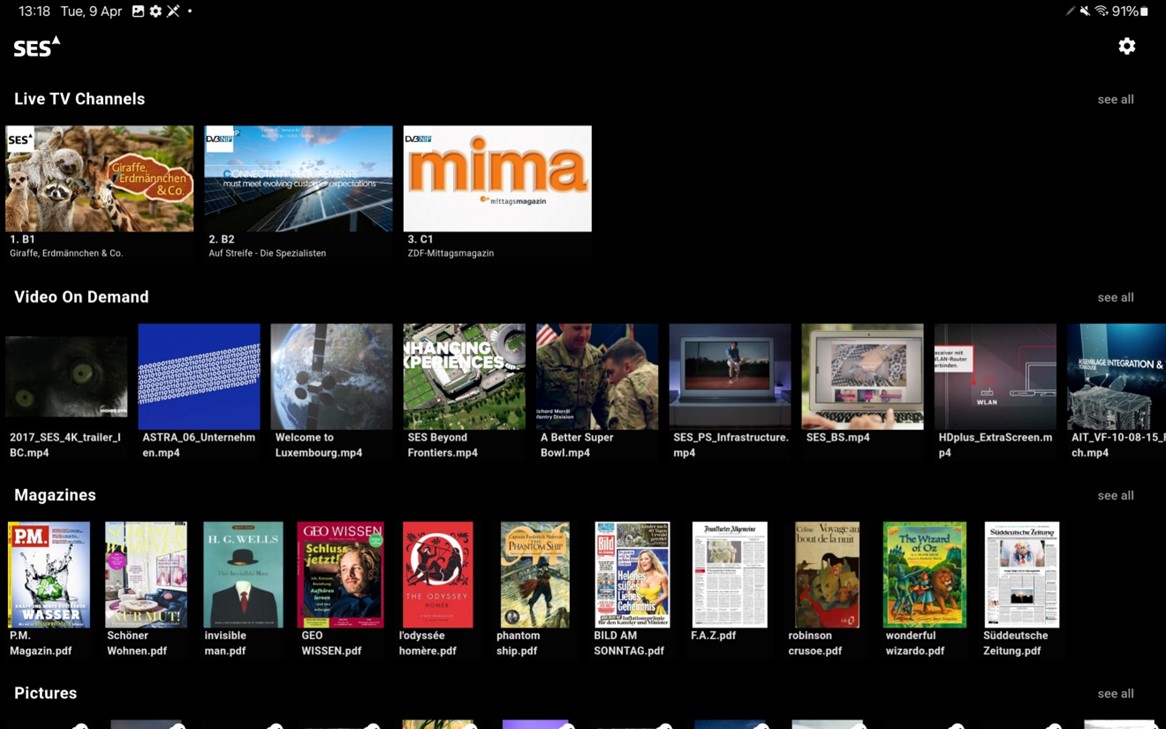
The demo ran on two ASTRA transponders at our key orbital position at 19.2 degrees East and showed live DVB-NIP transmissions received via an SES-developed DVB-NIP Gateway, displayed on an internally developed Android / Android TV DVB-I Client Application and on a first production ready DVB-I Television set.
The broadcasts included both live and offline content originating from our HQ in Betzdorf through an internally developed mABR server as well as from servers belonging to commercial industry partners.
Importance of DVB-NIP and DVB-I
DVB-NIP will play a key role in not only enabling broadcasters, content owners and OTT providers to be able to extend delivery of their content effortlessly into other modes of TV reception, but also in advancing content delivery for several other use cases.
Next Generation Direct-to-Home TV
Next Generation DTH is set to be one of the most important use cases for DVB-NIP, due to the inherent scalability that satellite broadcast brings to video distribution. DVB-NIP allows satellite to make the all-important step from digital to IP, providing a full integration of satellite technology with terrestrial OTT delivery to reach all consumer devices.
The satellite TV experience will be enriched natively with all the features that both our customers and their end users expect – the highest quality and reliable live and offline video reception, personalisation, best-in-class user experience, analytics and more.
Satellite-powered CDN: Edge Caching
DVB-NIP, at its core, is a file delivery system. It uses the same technologies that are used in terrestrial CDNs (Content Delivery Networks.) As a result, a DVB-NIP system can be compared to a satellite-powered CDN that delivers any content at infinite scale to caches at the edges of networks. These edges may be 5G tower sites or deep edge caches in telco networks. DVB-NIP perfectly supports use cases where satellite antennas are no longer located at the end-user’s home.
Mobile Entertainment
Edge Caches can also be located on moving platforms that often lack the connectivity of terrestrial installations. DVB-NIP transmissions can be received on larger vehicles, such as ships and ferries, buses and planes, and any content received can be made available to passengers on their own devices.
Education
DVB-NIP can be useful for remote education with satellite broadcasting helping overcome the issue where lack of education is linked to a lack of connectivity by delivering educational material in any file format directly to unconnected classrooms via satellite and then using Wi-Fi onto student laptops and PCs.
What’s Next for DVB-NIP?
“Proof Of Concepts” (POCs) for DVB-NIP are taking place now, and we expect the technology to become more widespread over the next few years. One thing is certain: DVB-NIP will shape the future of broadcasting, allowing content providers to blend the scale, efficiency and service quality of traditional broadcast networks with the interactive and one-to-one features of terrestrial IP networks, and SES will be one of those spearheading these standardisations.




